Case 17
- Wangpan Shi
- Jan 14
- 1 min read
Updated: Jan 23
A 30-year-old female was found to have a mass at superior half of the nasal septum. The tumor was found to be positive for synapotophysin.



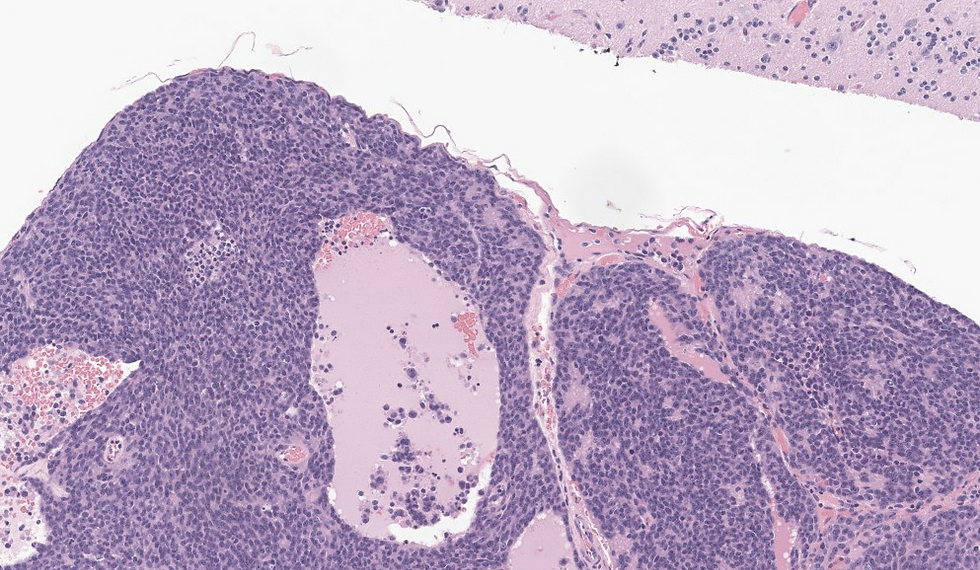
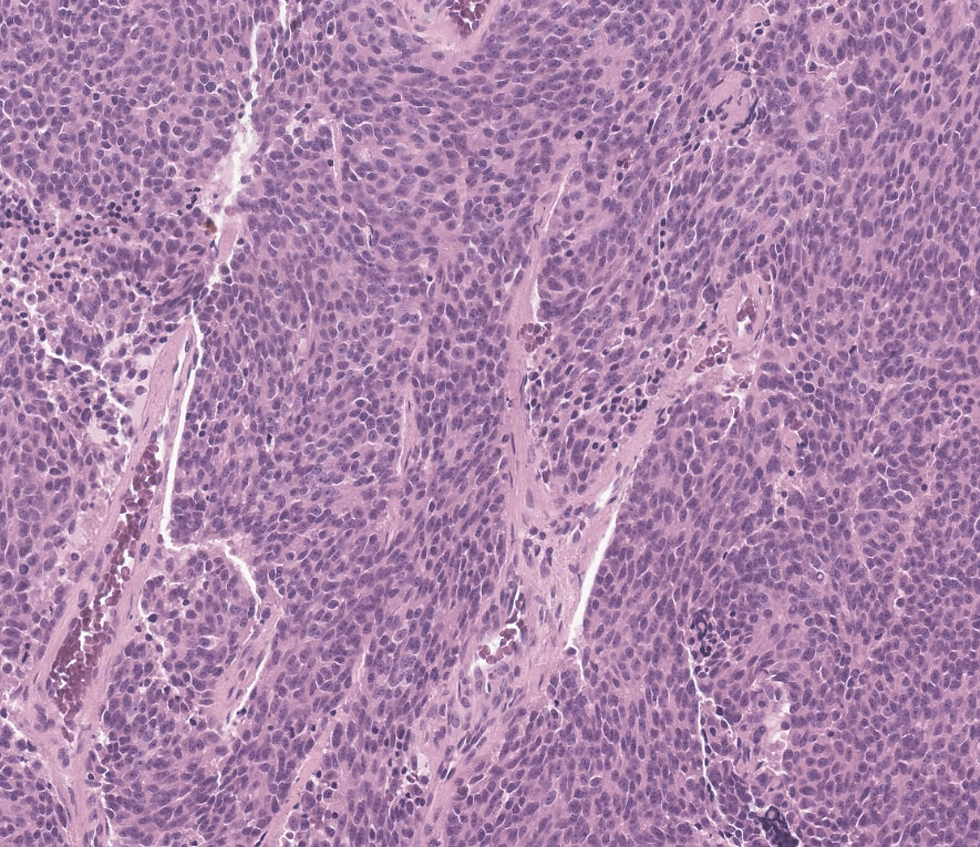
What is the diagnosis?
A: Small cell carcinoma
B: Ewing sarcoma
C: Alveolar RMS
D: Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma
E: Olfactory neuroblastoma
F: NUT midline carcinoma
Answer
This case is Olfactory neuroblastoma but the above lists are good differentials in small round cell tumors in sinonasal tract. Olfactory neuroblastoma derived from immature or progenitor olfactory epithelium cells and are arranged in nests, lobules, or sheets that are clearly delineated by a rich vascular stroma, usually in the submucosa. A salt-and-pepper nuclear chromatin characterizes the cells. In ONBs, fibrillary cytoplasm and interdigitating neuronal processes (neuropil) are characteristic. Flexner–Wintersteiner rosettes and Homer Wright pseudorosettes can be seen. High-grade tumours show a more sheet-like growth pattern. Rosettes by themselves are not diagnostic of ONB, although Homer Wright pseudorosettes with neuropil are nearly pathognomonic in the nasal cavity. In this case there are vaguely cules of Homer Wright pseudorosettes that does not have a true lumen without a cytoplasmic extension. ONB are typically positive for neuroendocrine markers and negative for keratin (1/3 can be positive). On the other hand, neuroendocrine neoplasms are always positive for keratin. SSTR2A can be positive in ONB. An important ddx here is sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma, which are negative for neuroendocrine markers.
Case credit: UCSD Pathology
Author: Wangpan Jackson Shi, MD

Comments